Big-IP: Sharepoint 2010 Monitor
While specing out a Sharepoint 2007 to 2010 migration I discovered that the default monitor created by the application template on our big-ip LTM load balancers does not work. In seeking a solution I ran across this gentleman’s blog with a custom external monitor but found that it didn’t really work. The solution to make it work was simple (as I explained on his blog in a comment). I went ahead and extended it to be more environment generic.
Copy this script to /user/bin/monitors/sharepoint2010.sh and chmod +x the file to use.
#!/bin/bash # A custom NTLM capable sharepoint (or other site capable) health script for your big-ip load balancers # Zachary Loeber 01/21/2011 # Save as /usr/bin/monitors/sharepoint2010.sh # Make executable using chmod 700 sharepoint2010.sh # The following variables should be set to get this to work properly # # URI: part of the site you want to use as your monitor (ie. _layouts/recyclebin.aspx) # LOOKFOR: what will be returned that shows the site is up (ie. deleted) # HOSTHEAD: the host header to use for the site (ie. sharepoint.corp.contoso.com) # NTLMUSER: an account which can access this uri (ie. [email protected]) # NTLMPASS: the password of the above user (ie. password1) # DEBUG: optional variable for debugging purposes, can be set to 0 or 1 # Log debug to local0.debug (/var/log/ltm)? # Check if a variable named DEBUG exists from the monitor definition # This can be set using a monitor variable DEBUG=0 or 1 if [ -n "$DEBUG" ] then if [ $DEBUG -eq 1 ]; then echo "EAV `basename $0`: \$DEBUG: $DEBUG" | logger -p local0.debug; fi else # If the monitor config didn't specify debug, enable/disable it here DEBUG=0 #echo "EAV `basename $0`: \$DEBUG: $DEBUG" | logger -p local0.debug fi # Remove IPv6/IPv4 compatibility prefix (LTM passes addresses in IPv6 format) IP=`echo $1 | sed 's/::ffff://'` # Save the port for use in the shell command PORT=$2 # Check if there is a prior instance of the monitor running pidfile="/var/run/`basename $0`.$IP.$PORT.pid" if [ -f $pidfile ] then kill -9 `cat $pidfile` > /dev/null 2>&1 echo "EAV `basename $0`: exceeded monitor interval, needed to kill ${IP}:${PORT} with PID `cat $pidfile`" | logger -p local0.error fi # Add the current PID to the pidfile echo "$$" > $pidfile #### Customize the shell command to run here. ### # Use $IP and $PORT to specify which host/port to perform the check against # Modify this portion of the line: # nc $IP $PORT | grep "my receive string" # And leave this portion as is: # '2>&1 > /dev/null' # The above code redirects stderr and stdout to nothing to ensure we don't errantly mark the pool member up # Send the request request and check the response curl -H "Host: $HOSTHEAD" -fNs --ntlm -k --user "$NTLMUSER:$NTLMPASS" \ "http://$IP:$PORT/$URI" | grep -i "$LOOKFOR" 2>&1 > /dev/null # Check if the command ran successfully # Note that any standard output will result in the script execution being stopped # So do any cleanup before echoing to STDOUT if [ $? -eq 0 ] then echo "UP" rm -f $pidfile if [ $DEBUG -eq 1 ]; then echo "EAV `basename $0`: Succeeded for ${IP}:${PORT}" | logger -p local0.debug; fi else rm -f $pidfile if [ $DEBUG -eq 1 ]; then echo "EAV `basename $0`: Failed for ${IP}:${PORT}" | logger -p local0.debug; fi fi # Debug if [ $DEBUG -eq 1 ] then #### Customize the log statement here if you want to log the command run or the output #### echo "EAV `basename $0`: Running for ${IP}:${PORT} using custom command" | logger -p local0.debug fi
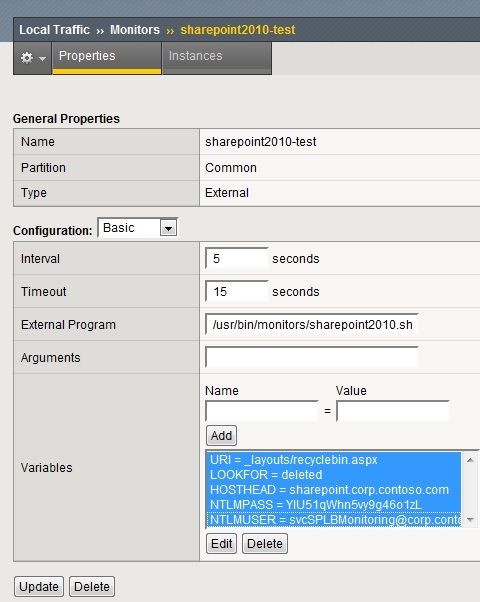
Here is an example health monitor configuration: